In healthcare facilities, medical gases play an essential role in patient care, from providing oxygen in intensive care units (ICUs) to delivering anesthesia in operating rooms. Ensuring the proper delivery of these gases, as well as detecting any potential issues in the gas supply system, is crucial for patient safety. That’s where medical gas alarms come into play. These sophisticated systems are designed to monitor and alert healthcare staff to any irregularities in medical gas supply, ensuring the reliability and safety of these life-sustaining gases.
In this article, we will explore what a medical gas alarm is, its components, how it works, and why it is a critical part of any healthcare facility’s infrastructure.
1. What is a Medical Gas Alarm?
A medical gas alarm is an electronic monitoring system that continuously tracks the pressure, flow, and status of medical gases used in a healthcare facility. It provides real-time alerts to medical staff if there are any deviations from the normal operating parameters, such as pressure drops, leaks, or overpressure conditions in the medical gas pipelines. These alarms are an integral part of a hospital’s medical gas pipeline system (MGPS), which delivers essential gases like oxygen, nitrous oxide, medical air, and vacuum to various points of use within the facility.
Medical gas alarms are typically installed in critical areas such as:
- Nurse stations
- Operating rooms
- Emergency rooms
- Intensive care units (ICUs)
They ensure that any problem with the gas supply is detected and addressed immediately, preventing potentially dangerous situations from escalating.
2. Why Are Medical Gas Alarms Important?
Medical gases, such as oxygen and nitrous oxide, are used in a wide range of medical procedures and treatments. A disruption in their supply could have serious consequences for patients. For example, if the oxygen supply to a patient on a ventilator is compromised, it could lead to life-threatening complications. Medical gas alarms help mitigate these risks by detecting issues early and allowing healthcare providers to take prompt corrective action.
Key Benefits of Medical Gas Alarms:
1. Ensuring Patient Safety:
Medical gas alarms help prevent accidents caused by gas leaks, pressure drops, or contamination in the gas supply. These alarms ensure that patients receive the correct amount of gas at the required pressure and purity levels.
2. Real-Time Monitoring:
Medical gas alarms provide continuous, real-time data on the status of the gas supply, allowing staff to monitor the system around the clock. This monitoring is critical in areas like operating rooms, where any interruption in the gas supply could lead to serious complications during surgery.
3. Early Detection of Issues:
The alarm system alerts healthcare personnel to potential problems before they become critical, such as a gas cylinder running low or a pressure drop in the oxygen supply line. Early detection allows for quick interventions and minimizes the risk of harm to patients.
4. Compliance with Healthcare Standards:
Medical gas alarms are required by various regulatory bodies, including NFPA 99 (National Fire Protection Association) in the United States and ISO 7396 in international settings. These systems help healthcare facilities comply with safety regulations and ensure that they meet industry standards for medical gas delivery.
3. Key Components of a Medical Gas Alarm System
A medical gas alarm system is composed of several key components, each playing a specific role in ensuring the safety and efficiency of the medical gas supply. Here’s a breakdown of the essential elements:
1. Pressure Sensors and Transducers:
-
-
- Pressure sensors are responsible for measuring the pressure of the medical gases within the pipeline. They detect fluctuations in pressure, such as drops or surges, and send this information to the alarm system.
- Transducers convert the physical pressure data into electronic signals, which are then processed by the alarm’s control unit.
-
2. Master and Area Alarms:
-
-
- Master Alarm: The master alarm monitors the entire medical gas pipeline system in the healthcare facility. It provides a centralized view of the gas supply, allowing facility managers and technicians to monitor all zones in the building. If any gas system malfunctions, the master alarm will alert personnel, often in a maintenance or engineering control room.
- Area Alarm: An area alarm monitors specific sections or areas of the medical gas pipeline system, such as operating rooms or patient wards. These alarms provide localized monitoring and alert staff to problems in specific areas, ensuring prompt responses where needed.
-
3. Visual and Audible Indicators:
-
-
- Visual Indicators: Medical gas alarms are equipped with light indicators, typically color-coded to reflect the severity of the issue. For instance, green lights often indicate normal conditions, while yellow or red lights signal a warning or critical alarm.
- Audible Indicators: In addition to visual alerts, medical gas alarms produce audible sounds to notify healthcare staff of any issues. The sound may vary in volume or intensity depending on the level of urgency.
-
4. Control Panel:
-
-
- The control panel is the central hub of the medical gas alarm system. It displays the status of the medical gas supply and provides real-time data on pressure levels, flow rates, and system integrity. Modern control panels are often equipped with touchscreen displays for easy navigation and control.
-
4. How Does a Medical Gas Alarm Work?
The medical gas alarm system is continuously connected to the medical gas pipeline system, monitoring the flow and pressure of the gases in real time. Here’s how it works:
1. Data Collection:
Pressure sensors are placed at various points along the medical gas pipeline. These sensors measure the gas pressure and send data to the control panel.
2. Monitoring:
The control panel processes the data from the pressure sensors and compares the current readings to pre-set thresholds for each gas. These thresholds represent the acceptable pressure range for each gas in the pipeline.
3. Triggering the Alarm:
If the pressure falls below or rises above the acceptable range, the control panel activates an alarm. Both visual (lights) and audible (sound) alarms will notify healthcare staff of the issue.
4. Responding to the Alarm:
Medical personnel are trained to respond to these alarms quickly. In the case of a minor issue, such as a drop in gas pressure, staff may check the system and make adjustments as needed. For more serious issues, such as a gas leak, emergency procedures are followed to ensure patient safety and resolve the problem.
5. Common Issues Detected by Medical Gas Alarms
Medical gas alarms are designed to detect a range of potential issues in the medical gas pipeline system. Some of the most common problems that these alarms help identify include:
1. Pressure Drops:
Pressure drops in the pipeline can occur if there is a leak, a blockage, or if a gas cylinder is running low. A drop in pressure can lead to insufficient gas delivery, which can compromise patient care, particularly in cases where oxygen or anesthesia is being administered.
2. Overpressure:
Overpressure occurs when the gas pressure exceeds the recommended level. This could be caused by faulty regulators or excessive gas supply. Overpressure can damage medical equipment and pose a safety risk to patients and staff.
3. Gas Leaks:
Gas leaks in the pipeline are dangerous and need to be addressed immediately. Medical gas alarms detect leaks by identifying unusual pressure drops or fluctuations in the system.
4. Contaminated Gas Supply:
While rare, contamination of medical gases can occur if filters fail or if there is a breach in the pipeline. Medical gas alarms can help detect such issues by monitoring changes in gas flow or pressure.
6. Regulations Governing Medical Gas Alarms
Due to the critical role medical gas alarms play in patient safety, their design, installation, and operation are subject to strict regulations and standards. Some of the most notable regulations include:
1. NFPA 99 (United States):
The NFPA 99 code is a healthcare facilities code that outlines the minimum safety requirements for medical gas pipeline systems, including medical gas alarms. It covers the design, installation, testing, and maintenance of these systems to ensure patient safety.
2. ISO 7396-1 (International):
ISO 7396-1 sets international standards for medical gas pipeline systems, including requirements for monitoring and alarm systems. The standard specifies how alarms should be installed, how they should operate, and the acceptable limits for gas pressure and flow.
3. European Pharmacopoeia (Europe):
The European Pharmacopoeia outlines standards for the purity and quality of medical gases. Medical gas alarms play a key role in ensuring that the gases delivered meet these purity standards.
7. Introduction of Amcaremed medical gas alarm
AmcareMed medical gas alarm system includes of area alarm and master alarm.
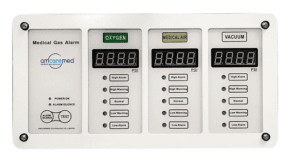
1.AM-AR3 series of medical gas area alarm
AM-AR3 series of medical gas area alarms are installed for monitoring medical gas pressure at hospitals, nurse stations, operating rooms…etc. It can actively display the pressure number of the monitoring gas including oxygen, air, vacuum, nitrous oxide, carbon dioxide, and nitrogen. Also, the alarm point can be set on the basis of the parameters using demand. Transfinite alarm ensures supplier gas pressure is normal. Moreover, this type of gas alarm is equipped with the RS-485 communication interface, which can be connected to the master alarm box and the system hosted by the network.
2. LCD medical gas area alarm
LCD medical gas area alarm is active displays the pressure number through a 10.1-inch LCD screen. In this case, the user can set the alarm point parameters through touching screen. When the parameter value is exceeded, alarming the maintenance staff ensures normal gas supplier pressure in the hospital. Paragraph 2 shows an area alarm.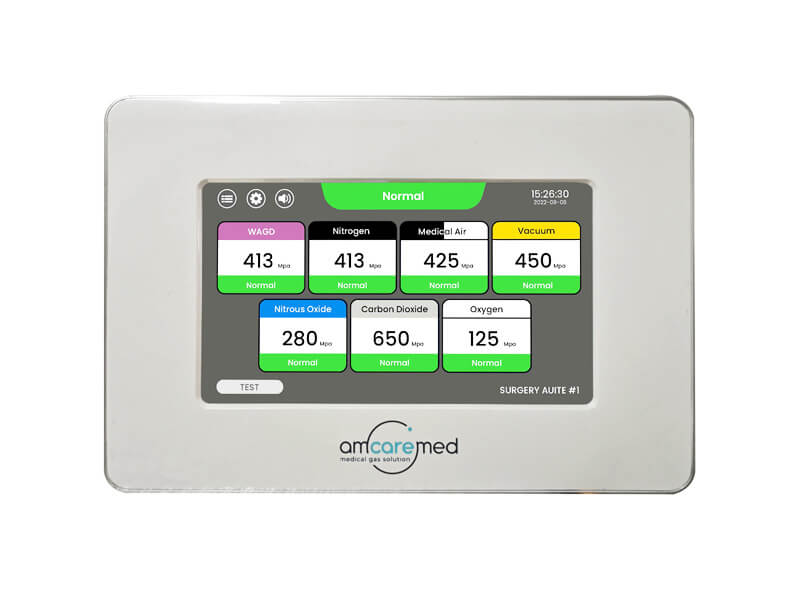
Both of them support pressure sensor failure detection, sound and light alarm, and buzzer silence. Besides, all parameters can field debugging or setting.
AmcareMed medical gas area alarm could be able to interface with most building management systems with the use of additional equipment. The alarm panel is enclosed in a steel box and is designed to accept an electrical input range of 100-240 VAC.
8. Conclusion
Medical gas alarms are an essential safety feature in any healthcare facility, providing real-time monitoring and alerts that help ensure the continuous and safe delivery of life-saving gases. These systems play a vital role in protecting patients and staff from the risks associated with gas leaks, pressure fluctuations, and system malfunctions.
As healthcare technology continues to advance, so too does the sophistication of medical gas alarms, with modern systems offering enhanced monitoring capabilities, automation, and integration with hospital management systems. For healthcare providers, understanding and maintaining medical gas alarms is critical to ensuring the safety, reliability, and efficiency of their medical gas systems.
